
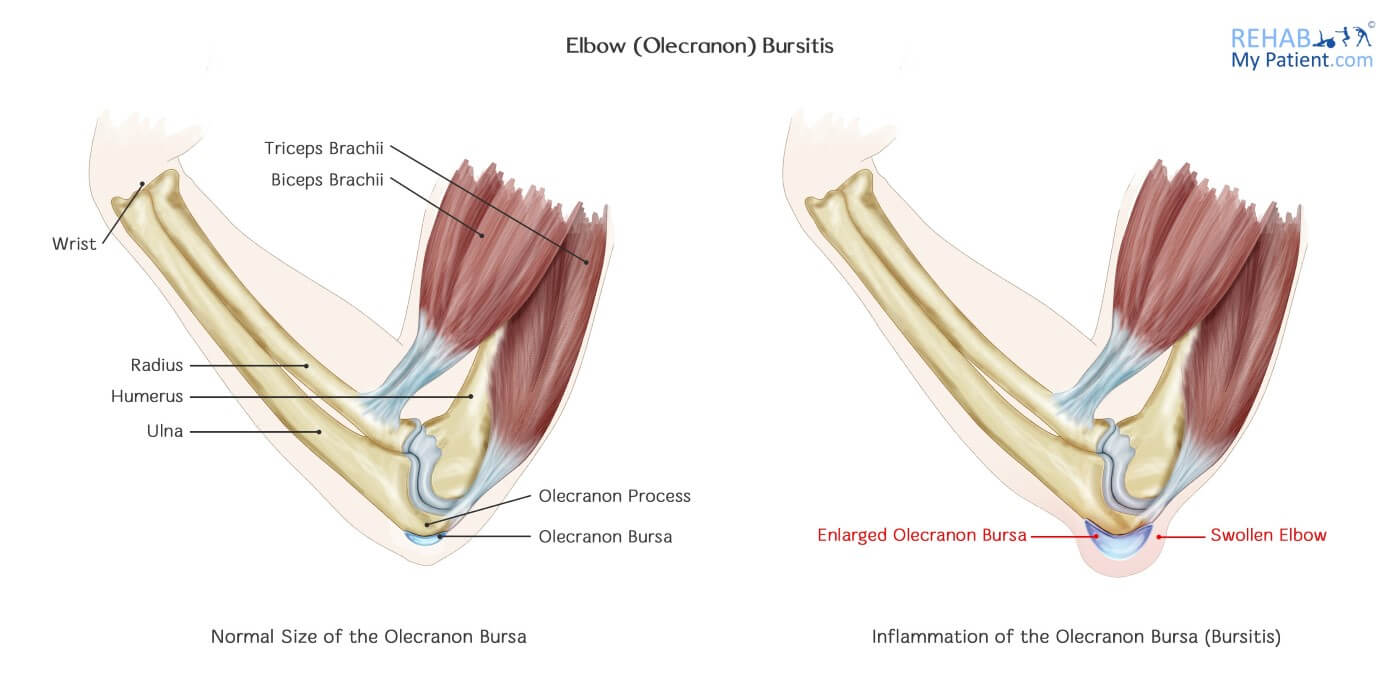
Bursae are slippery, thin sacs that are located throughout the entire body. They serve as a cushion between the soft tissues and the bones. They are composed of a small amount of lubricating fluid that lets the skin move freely above the bone underneath.
The olecranon bursa lies in the middle of the pointy end (base) of the elbow. Most of the time, the olecranon bursa is flat. When it becomes inflamed and irritated, more fluid accumulated in the bursa and bursitis ends up developing.
Sometimes olecranon bursitis is called student’s elbow, as students who spend long hours writing tend to rest their elbows on a desk. This causes friction to the elbow which can irritate the bursa. So it may not just affect students, but anyone who spends long hours writing or resting their elbows on a hard surface.
Elbow (Olecranon) Bursitis Anatomy
Three bones joint together to complete the elbow joint. The bone in the upper part of the arm is referred to as the humerus. Two bones from the forearm come together to make up the lower elbow part of the arm. All of the bones have a distinct shape. Ligaments that are connected to the bones work to keep everything in proper alignment.
The elbow is a ball-and-socket joint and hinge joint and a hinge joint. As the muscles relax and contract, two distinct motions occur in the elbow. Bending happens through the hinge joint that lets the elbow straighten and bend, which is known as extension and flexion. Rotation happens from the ball-and-socket joint allowing the hand to rotate the palm down and up, which is known as supination and pronation.
How to treat elbow bursitis:
- Aspiration
If it is suspected that the bursitis is the result of an infection, it might be recommended that the bursa is aspirated with a needle. This office procedure helps to relieve the symptoms you are dealing with and provide the doctor with a sample of the fluid for further examination to identify if there are any bacteria growing in the fluid. It also alerts the doctor to the need for any antibiotics for fighting the infection.
- Antibiotics
Again if the bursitis is caused by infection rather than abrasion, an antibiotic could be used to help prevent the infection from spreading and getting any worse. The type of antibiotic prescribed will work to treat a number of different infections at this point in time.
- Change in Activities
Avoid engaging in any activities that cause you to apply direct pressure to the swollen region. Stop putting pressure through the elbow!
- Medication
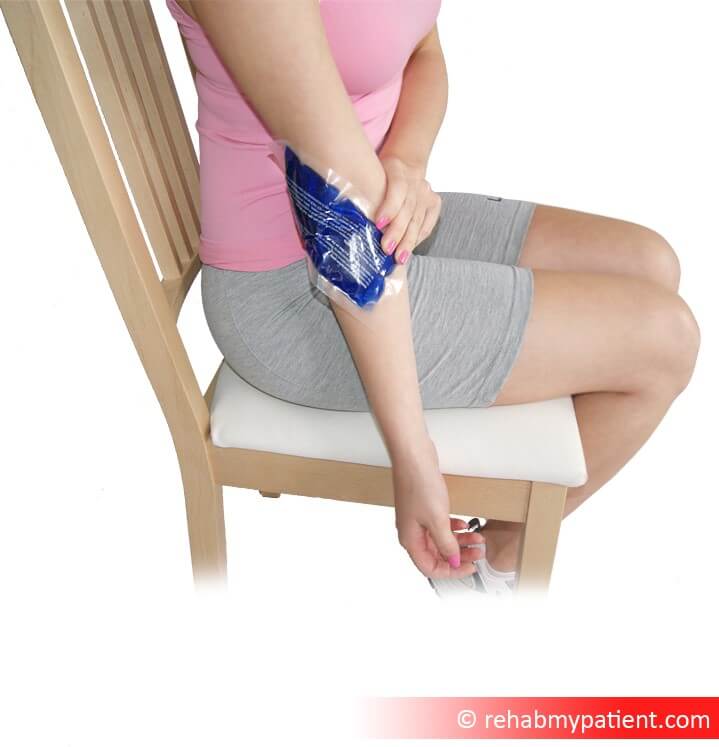
Ibuprofen and various other anti-inflammatory medications are often used to help minimize swelling and relieve a whole host of other symptoms associated with the condition. An alternative to using anti-inflammatories is using an ice pack on the elbow. This is a much more natural alternative, but can take a few weeks of using it so be persistent.
- Elbow Pads
Elbow pads help provide the elbows with the cushioning they need.
Tips:
- Hard blows to the tip of the elbow could end up causing the bursa to produce an excess of fluid and end up swelling.
- Reduce resting your elbows on tables or chair arms.
- Bursa sacs can become infected without ever having an obvious skin or abrasion injury.
- Gout and rheumatoid arthritis are often associated with bursitis.
- For those who work as HVAC technicians and plumbers, the risk of developing the condition tends to increase.
- Leaning on the elbow tip for a long period of time will cause swelling in the bursa.
- Applying ice to the bottom of the elbow over a period of six weeks can help improve the condition significantly.

Sign Up
Sign up for your free trial now!
Get started with Rehab My Patient today and revolutionize your exercise prescription process for effective rehabilitation.
Start Your 14-Day Free Trial