
General information
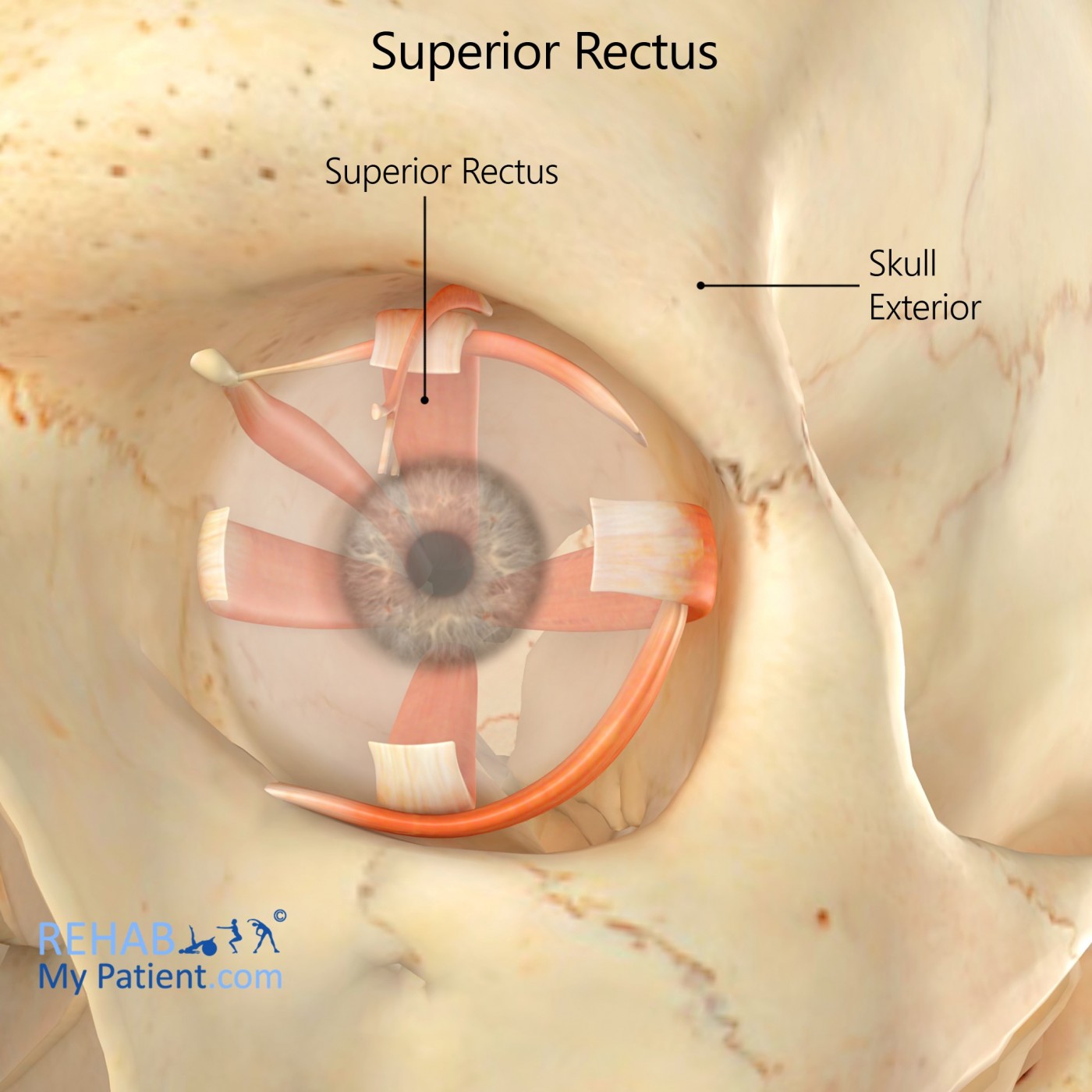
The superior rectus is a muscle that is in orbit. As one of the extraocular muscles, it is innervated from the superior division of the oculomotor nerve. When in its primary position, the muscle’s primary function is elevation, but it is also responsible for adduction and intorsion.
Literal meaning
Straight above.
Interesting information
When the eye is in a fully abducted position, the superior rectus is the only muscle that can elevate it. Traumatic injuries of the rectus muscle tend to be quite rare. Rupturing of the inferior rectus muscle is often referred to as a blowout fracture. When an injury has been described following a trauma, it is often associated with extensive ocular and orbital damage.
Severed or disinserted muscles are one of the main complications for strabismus surgery. When looking into cases like these, the eye should not be forced into the opposing field of action where the suspected muscle is. It could cause the muscle to slip back and penetrate the site within Tenon’s capsule.
Origin
Superior part of the common tendinous ring surrounding the optic canal.
Insertion
Superior surface for the anterior portion out of the sclera.
Function
Adduction, elevation and intorsion of the eye.
Nerve supply
Oculomotor nerve.
Blood supply
Supraorbital artery’s muscular branches from the ophthalmic artery from the internal carotid artery.
Relevant research
Authors attempted to establish a surgical treatment for strabismus in cases where either the inferior rectus or the superior rectus were diagonally transposed. The safety and effects of the procedure were studied. 18 operations, using local anaesthetic with eye drops, were conducted on 17 patients. 10 of those cases were on patients that have superior oblique palsy. During the operation, diplopia was checked with the patient’s cooperation. Both eye deviation and clinical findings were examined in the observation period.
Following the first operation, diplopia had vanished in 10 cases and dramatically improved in the remaining seven. On average, the correction was 6.2 degrees to the primary position. Of the seven instances where the palsy received nasal recession for the inferior rectus muscle, correction averaged 6.4 degrees and vertical deviation changed 1.8 degrees. In no instances did the condition worsen or cause any complications for the patient.
Nemoto Y, Kaneko H, Sakaue T, Kobota N, Maruo T, Oshika K. Skew transposition of vertical rectus muscles for excyclovertical deviation. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2000;44(4):428-432. doi:10.1016/s0021-5155(00)00175-1.
Superior rectus exercises
Eye massage
Eye massage works to help relieve strain and stress while massaging the muscles that surround and support the eyeball. Performing the exercise once per day will make sure the muscles are stretched and limber. Find a position that is comfortable and close the eyes. Place the thumbs gently below the eyebrows and on the inside corners of the eyes close to where the eyes meet the nose. Place the other four fingers on the forehead. Apply pressure inward using the thumbs and count to four. Using the index finger and thumb of either hand, massage the nose’s bridge and count to four as pressure is applied. Repeat the exercise four times.
Sign Up
Sign up for your free trial now!
Get started with Rehab My Patient today and revolutionize your exercise prescription process for effective rehabilitation.
Start Your 14-Day Free Trial