
General information
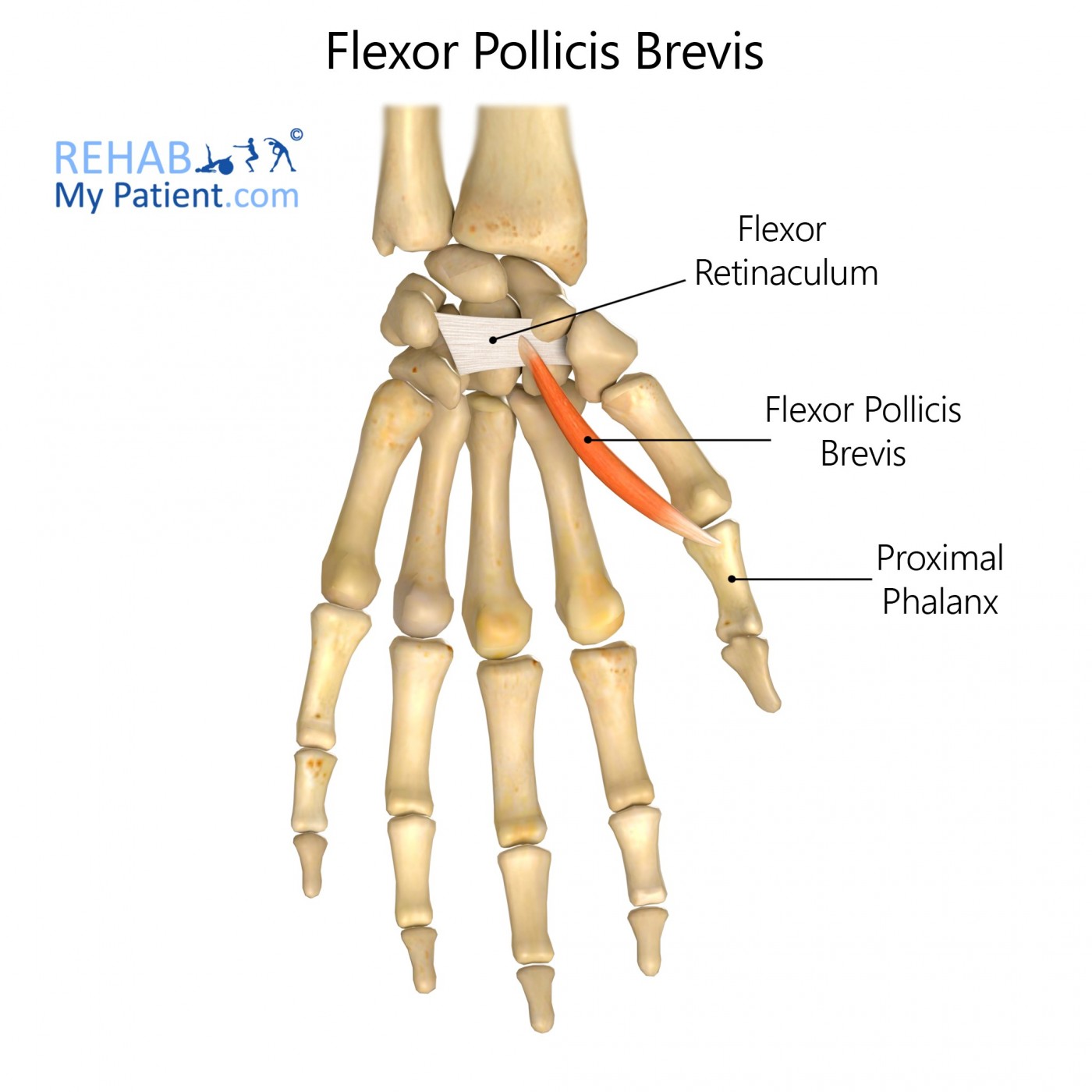
Flexor pollicis brevis is one of three thenar muscles situated in the palm of the hand.
Literal meaning
The short muscle that flexes (bends) the thumb.
Interesting information
This singular muscle is composed of two distinct parts: superficial and deep. The joining of these two parts forms a tendon which attaches to the thumb.
The fleshy soft tissue on the palm of the hand near the thumb is referred to as the thenar eminence. It is formed by extensor pollicis brevis, flexor pollicis brevis, abductor pollicis brevis, and opponens pollicis.
To test the strength and function of flexor pollicis brevis, sit in a chair with one hand resting on a flat surface and your palm facing up. Place your opposite hand on the fleshy section of palm at the base of your thumb and apply gentle pressure. Flex (bend) your thumb against that pressure. You should be able to feel the movement of flexor pollicis brevis. If the muscle is functioning properly, you will overcome the resistance easily.
Hand injuries are a very common occurrence and they account for a significant percentage of emergency room visits. The human hand is a very complex structure so proper diagnosis of injury requires extensive knowledge of hand anatomy and physiology. Injuries to flexor pollicis brevis can include strain, tears, atrophy, infectious myositis, and overuse. Injury should be suspected when hand or thumb pain is present or if there is decreased flexion of the thumb.
Origin
Flexor retinaculum and the trapezium.
Insertion
The base of the proximal phalanx of the thumb (radial side).
Function
Flexes the pollux (thumb).
Nerve supply
Median nerve and ulnar nerve (C8, T1)
Blood supply
Radial artery (superficial palmar branch)
Relevant research
This study was a 13 year review of surgically transposing flexor pollicis brevis in order to treat the loss of thumb opposition as a result of late stage median nerve injury. The results of the study showed that all of the patients receiving this treatment regained thumb opposition function without significant post-operative complications. Thus, transposition of flexor pollicis brevis to restore thumb opposition is a highly effective surgical method.
Zhu W, Wang SH, Zhang YL, Wei JN, Tian GL (2006). “Restoration of thumb opposition by transposing the flexor pollicis brevis muscle: thirteen-year clinical application”. Chin Med J (Engl). 5;119(3):207-10.
Flexor pollicis brevis has also been indicated in the treatment of ulnar nerve paralysis which causes loss of thumb and index finger coordination (pinch power). Flexor pollicis brevis adductorplasty shows promise as an alternative method for restoring adductor pollicis function following ulnar nerve paralysis.
Uralo?lu M, Orbay H, Açar HI, Sensöz O. (2006). “Flexor pollicis brevis adductorplasty: an alternative method in ulnar nerve paralysis”. Ann Plast Surg. 57(1):110-4.
Flexor pollicis brevis exercises
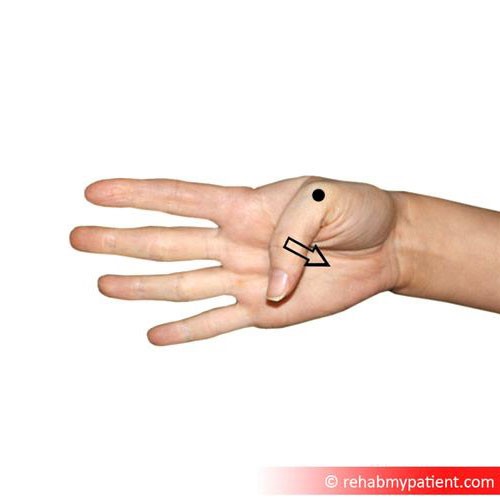

Hold your hand out in front of you with your palm facing up. Extend your fingers and thumb and slowly bring your thumb to the center of your palm while keeping the fingers extended. Hold for five second then extend the thumb outwards again. Repeat this exercise 30 times and then switch to your opposite hand.
For this exercise you will need a tennis ball, or a circular object of similar size. Hand putty also works really well. Hold the ball in the palm of your hand with your arm extended away from your body. Your thumb should be on top of the ball. Squeeze the ball as hard as you can and hold for ten seconds then relax. Repeat five times.
Sign Up
Sign up for your free trial now!
Get started with Rehab My Patient today and revolutionize your exercise prescription process for effective rehabilitation.
Start Your 14-Day Free Trial