
Concussions are traumatic brain injuries that alter the manner in which your brain functions. Most of the time, the effects are only temporary, but they can include problems with concentration, judgment, headaches, memory and coordination. Even though concussions are often the direct result of a blow to the head, they can also be the result of the upper body and the head being shaken violently. Injuries cause a tremendous amount of consciousness lost, but the majority of concussions don’t. It is because of this that a lot of people don’t even realize they have a concussion to begin with.
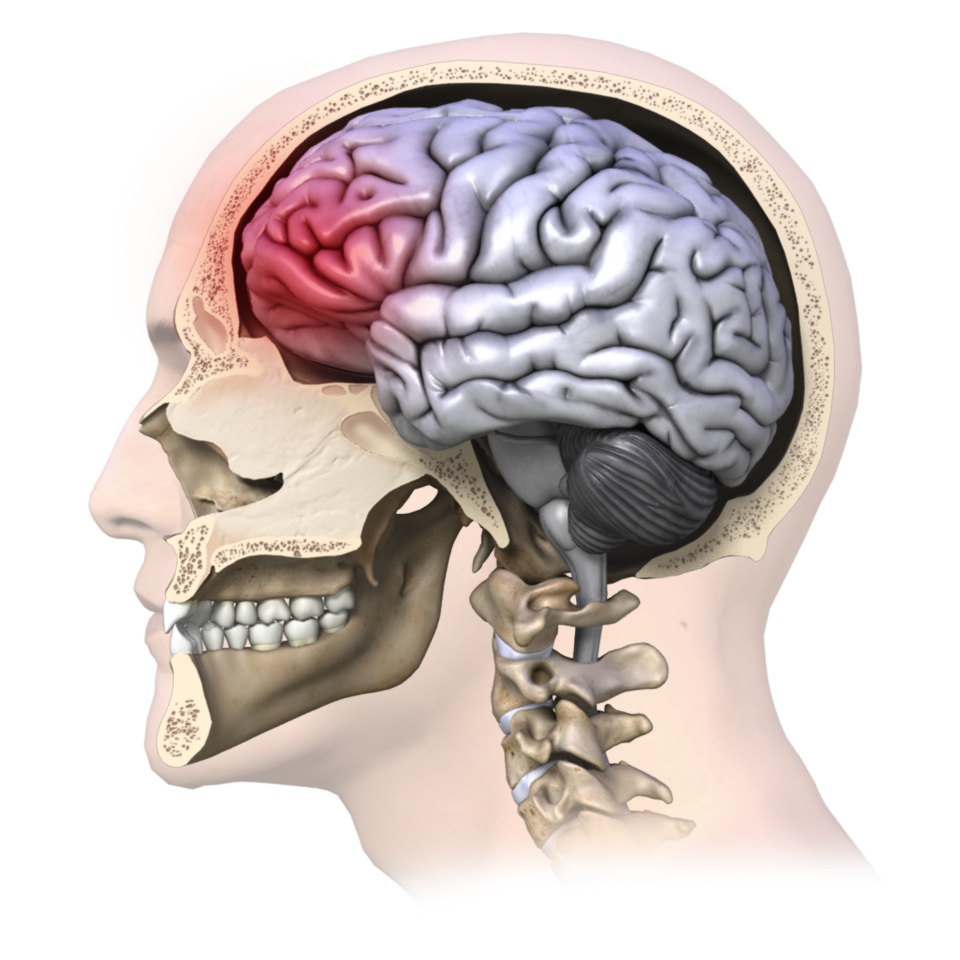
Concussions are quite common, especially in those who play contact sports. Such sports where heads can easily butt together between players is most common, for example rugby, hockey and football. Boxing is the most common sport for concussion. Every concussion will cause your brain to become injured to some degree. The injury needs time to heal and rest. The majority of concussions are mild and the individual is able to make a full recovery.
Following a concussion, if you start to notice any vomiting, nausea, change in vision, or strong headache, you should get to hospital straight away for further tests.
Concussion Anatomy
Blows to the head, such as that of what a quarterback might receive when a defender slams their helmet into them, can cause the brain to move forward, backward and rotate in the skull, which will cause a distortion in the axons connecting the neurons in the brain. In normal neurons, the axon is not distorted or otherwise broken. After the blow, the axon can bend or twist, which will cause an interruption in the communication between the neurons. If the concussion is too severe, the axon will swell and disintegrate. The axons that are not as severely damaged will return to normal.
How to Treat a Concussion:
1. Rest
One of the best ways to allow your brain to recover from the concussion is to rest. Children need to rest both mentally and physically. Avoiding any general physical exertion, in addition to any activities requiring mental concentration, such as that of watching television, playing video games, using a computer and texting. Workloads in school should be reduced temporarily.
2. Pain Relievers
For those dealing with a headache, use acetaminophen to help alleviate the pain. Avoid ibuprofen and aspirin as they can increase the potential of bleeding.
3. Refrain from Contact Activities
If your child or you sustained the injury from participating in competitive sports, you want to find out when it is safe to return to the activity. Resuming sports too quickly poses an increased risk of developing a second concussion that can lead to lasting and potentially fatally injuries to the brain. Some sports have a mandatory rest period for a number of weeks following concussion. The reason is that should a second concussion occur, this can significantly increase the danger of a bleed on the brain.
Tips:
1. Participating in high-impact sports increases your risk of ending up with a concussion. Lack of proper safety equipment and direct supervision when engaging in contact sports can cause concussions to occur.
2. Motor vehicle collisions are a leading cause of concussions within the US.
3. Children and older individuals are prone to concussions from falling down, especially if the head hits a curb or pavement.
4. For those who have been the victim of a concussion previously, the chances of getting another one in the future increase significantly.
5. Soldiers involved in combat are prone to concussions from the line of duty.
6. Never ever drink alcohol following a concussion.
Sign Up
Sign up for your free trial now!
Get started with Rehab My Patient today and revolutionize your exercise prescription process for effective rehabilitation.
Start Your 14-Day Free Trial