
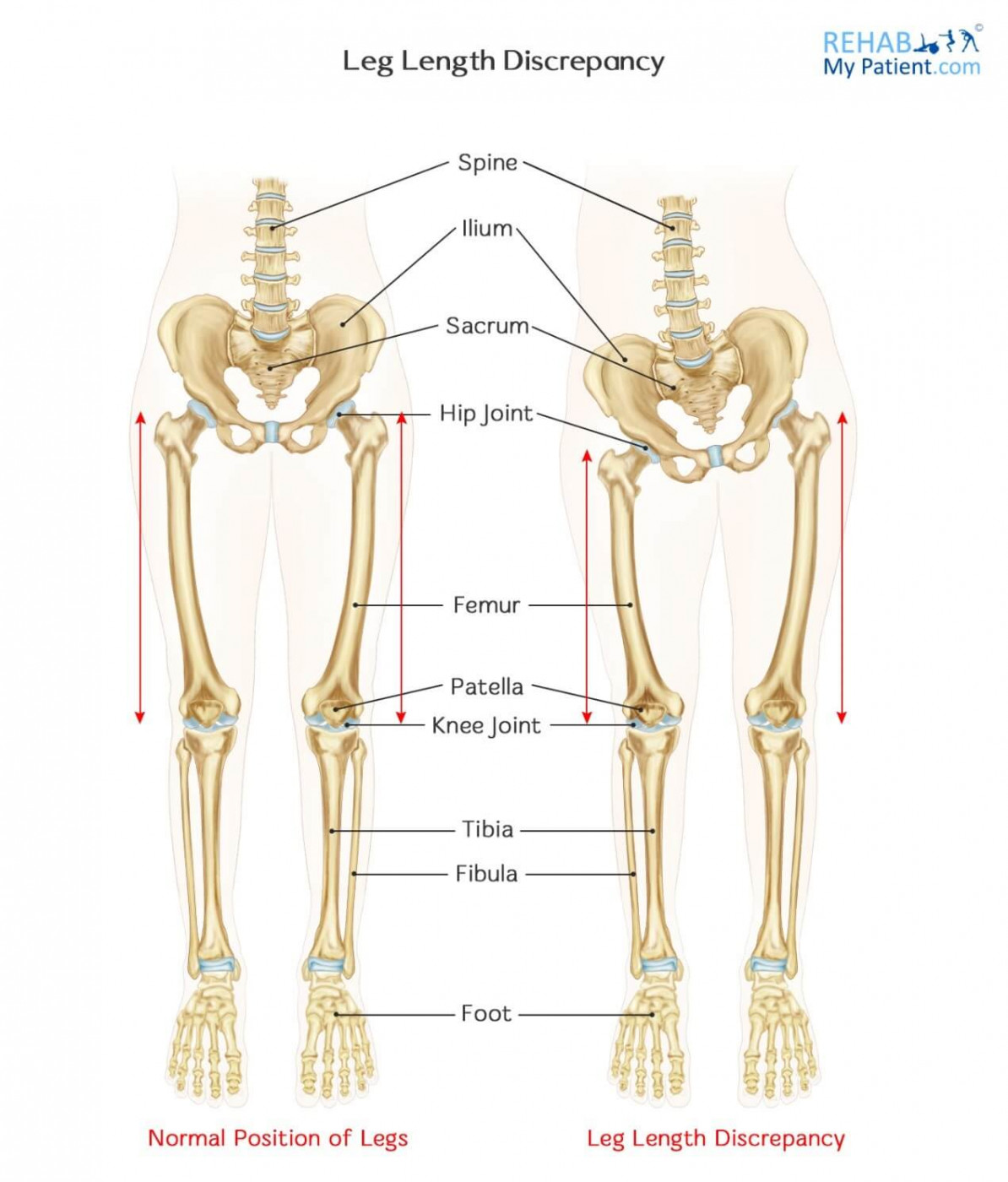
It is not uncommon to have one leg that is longer than the other, and this is referred to as a leg length discrepancy. Typical differences in leg length can range from one millimeter to more than six centimeters. The larger the discrepancy is, the more you will have to compensate their normal posture and walking patterns in their everyday life, which can cause any number of symptoms, such as knee, hip and ankle problems and functional scoliosis (curvature of the spine).
Two types of leg discrepancies exist:
- Structural discrepancies occur when either the shinbone or the thigh in one of the legs is shorter than the other leg.
- Functional discrepancies occur when the lengths of the legs are equal, but the symmetry is altered somewhere above the leg, which disrupts the leg symmetry. Developmental dislocation of the hip can cause this type of discrepancy.
It’s quite normal to have one leg slightly longer than the other, and this is compensated by the pelvis or the spine which curves just slightly to align the body. Typically anywhere up to 0.5cm leg length discrepancy is considered acceptable, or within normal limits. Over 0.5cm, then problems can occur.
The first issue is the spine usually has to curve to compensate for a leg length issue. This is known as a scoliosis. Small curvatures are again very common, but if the leg length issue is severe, then you may end up with a more pronounced curvature which would need expert attention.
True structural leg length discrepancies generally occur during growing years, so are developmental. One leg just grows slightly longer than the other. Asymmetry in the body is quite normal.
Functional leg length discrepancies (where the bones are the same length but one leg is still shorter/longer) occur for any number of reasons. It might be related to a sprained ankle as a child, or a twisted knee, or it might be the way you stand as an adult constantly favoring one leg to weight bear.
Leg length discrepancies can also occur after hip surgery. This is due for two reasons… 1. The surgeon may have inaccurately cut the thigh bone (femur) too short/long. Or quite often the hip surgery cuts through the lateral buttock muscles, which support the leg. Weakness in these muscles causes the hip to drop slightly, and can present as a noticeable limp on walking, known as a Trendelenburg Gait.
Leg Length Discrepancy Anatomy
The leg is the lower limb within the body responsible for supporting the body when standing. It provides you with the ability to walk, jump, run and engage in any number of other movements. The leg extends from the hip joint all the way to the ankle, which includes the largest of all bones in the body. There are five sections that make up the leg: knee, upper leg, lower leg, foot and ankle.
About 20 muscles exist in the lower part of the leg. They do everything from helping to raise the lower leg to wiggling the toes. Many of the muscles that power the movement in the foot begin as high as the back part of the knee and extend all the way down to the foot.
How to Treat Leg Length Discrepancy:
- Prosthetics
These devices, which are often used to treat children who has had to undergo an amputation, might be satisfactory for those who have a large discrepancy. Often, these individuals won’t benefit from other types of leg lengthening or shortening procedures.
- Orthotics
Shoe lifts can be used for treating discrepancies ranging from two to six centimeters. Heel wedges can also be used. In-soles with heel wedges might be used too. For severe cases, you can seek a hand-crafted shoe maker who will be able to put a higher heel on one side of your shoe.
- Epiphysiodesis
This procedure works to slow the growth rate of the longer leg, which allows the shorter leg time to catch up. The operation creates a bony ridge, usually by repositioning a bone block in the region tethering the growth plate, which prevents future growth. This is drastic and should be carefully considered if this treatment is necessary.
- Bone Resection
This operation involves removal of a section of bone to help equal out both sides. It can be performed in either adults or children who are done growing. This is drastic and should be carefully considered if this treatment is necessary.
Tips:
- Injuries, such as with a fracture damaging the cells that help the bone grow, occur in one leg, while the other bone continues to grow normally.
- Diseases of the bone can injure regions of the bone where the growth occurs, which causes a discrepancy over the course of time.
- Some children are bone with unequal or bowed tibias.
- Functional discrepancies can result from congenital problems altering the alignment of the hips.
- Cerebral palsy causes problems with posture and alignment, which can lead to functional discrepancies.
Sign Up
Sign up for your free trial now!
Get started with Rehab My Patient today and revolutionize your exercise prescription process for effective rehabilitation.
Start Your 14-Day Free Trial