
General information
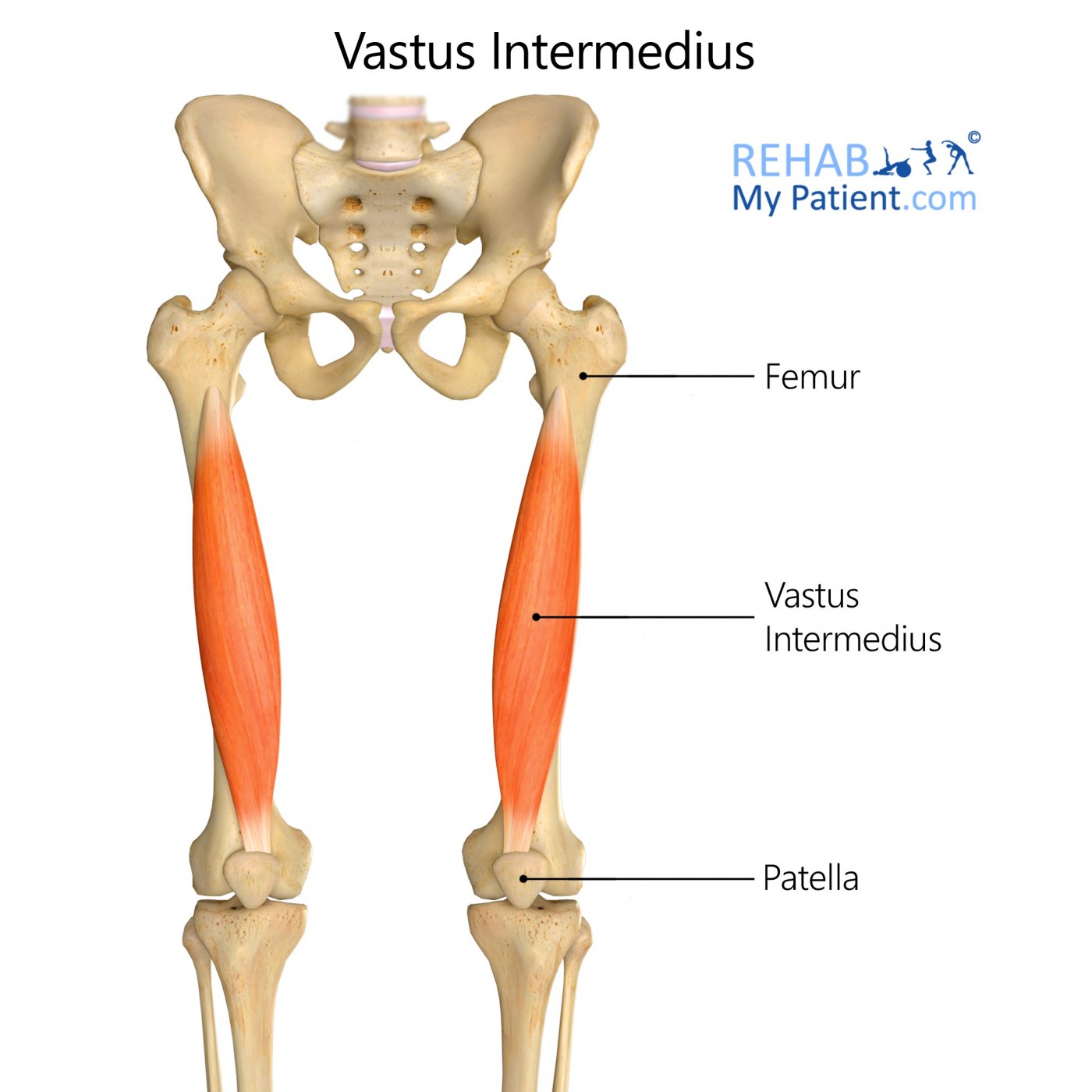
This muscle arises out of the lateral and front surfaces of the body for the femur within the upper two-thirds. It sits under the rectus femoris and the lower portion of the lateral intermuscular septum. The fibres end up in a superficial aponeurosis, which works to form the deep portion of the quadriceps femoris tendon.
Literal meaning
Enormous muscle in the middle.
Interesting information
A charley horse or dead leg is a contusion or bruise that is caused from a sharp impact from the muscle being crushed into the thigh bone. Even though it might be seen as a minor injury, it is imperative that a proper diagnosis is performed right from the start. If you try exercising on an injury, you could prevent it healing, leading to permanent damage. If heat is applied to the muscle too early, myositis ossificans can occur.
A quadriceps strain occurs when one of the muscles gets torn. It might range from a mild discomfort all the way to a full-blown tear of the majority of the muscle. A strain is often graded as a 1, 2 or 3, based upon the severity of the injury. Grade 1 strains are milder and don’t always require a cessation of training during the injury. A grade 3 strain, involving severe, complete rupture of the muscle, will cause immediate burning or stabbing pain and inability to walk, followed by severe bruising 2-3 days after the injury, and will require immediate treatment.
Origin
Proximal two-thirds for the lateral and anterior surfaces of the femoral shaft.
Lower portion of the lateral intermuscular septum.
Insertion
Tibial tuberosity.
Function
Knee extension.
Nerve supply
Femoral nerve L2-L4.
Blood supply
Femoral artery, deep femoral artery, transverse and descending branches out of the lateral circumflex artery and the branches of the genicular anastomoses surrounding the knee from proximal to distal.
Relevant research
This study discusses several case studies of patients who have been diagnosed with isolated vastus intermedius rupture. Two of the three patients admitted to steroid use. Two underwent surgery, whereas one patient only presented for medical attention nine months after the original injury and healed up with non-operative treatment. The study authors commented that isolated vastus intermedius rupture is difficult to detect both clinically and peri-operatively. The rectus femoris is intact, meaning the vastus intermedius rupture can easily be missed. Most literature covers rupture of the quadriceps tendon, but not the vastus intermedius specifically.
Thompson, Simon & Bird, J. & Somashekar, Naresh & Dick, Elizabeth & Spicer, D.. (2008). Investigation and treatment for isolated vastus intermedius rupture. Injury Extra. 39. 232-234. 10.1016/j.injury.2007.11.421.
Vastus intermedius exercises
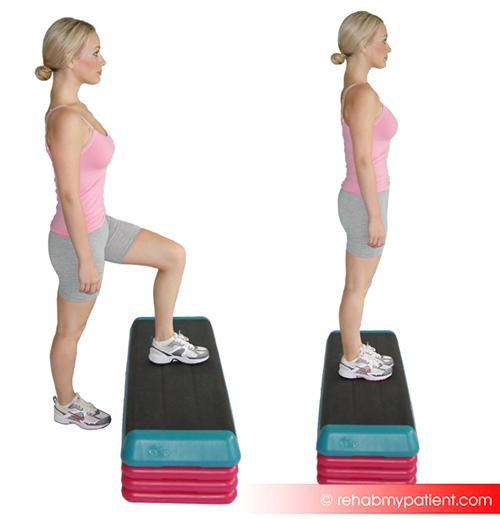
Step-ups
For this exercise, a firm surface to step on is required. It needs to be elevated at least eight inches or more based upon your individual abilities. Use free weights to add more of a challenge to the exercise. Begin standing off the elevated surface with the body in front of it. If using weights, hold one in each hand. With one foot, in a controlled and slow manner, step onto the surface that is elevated. Follow with the other foot and step down leading with the same foot. Try to perform three sets of 10 repetitions each side.

Sign Up
Sign up for your free trial now!
Get started with Rehab My Patient today and revolutionize your exercise prescription process for effective rehabilitation.
Start Your 14-Day Free Trial