
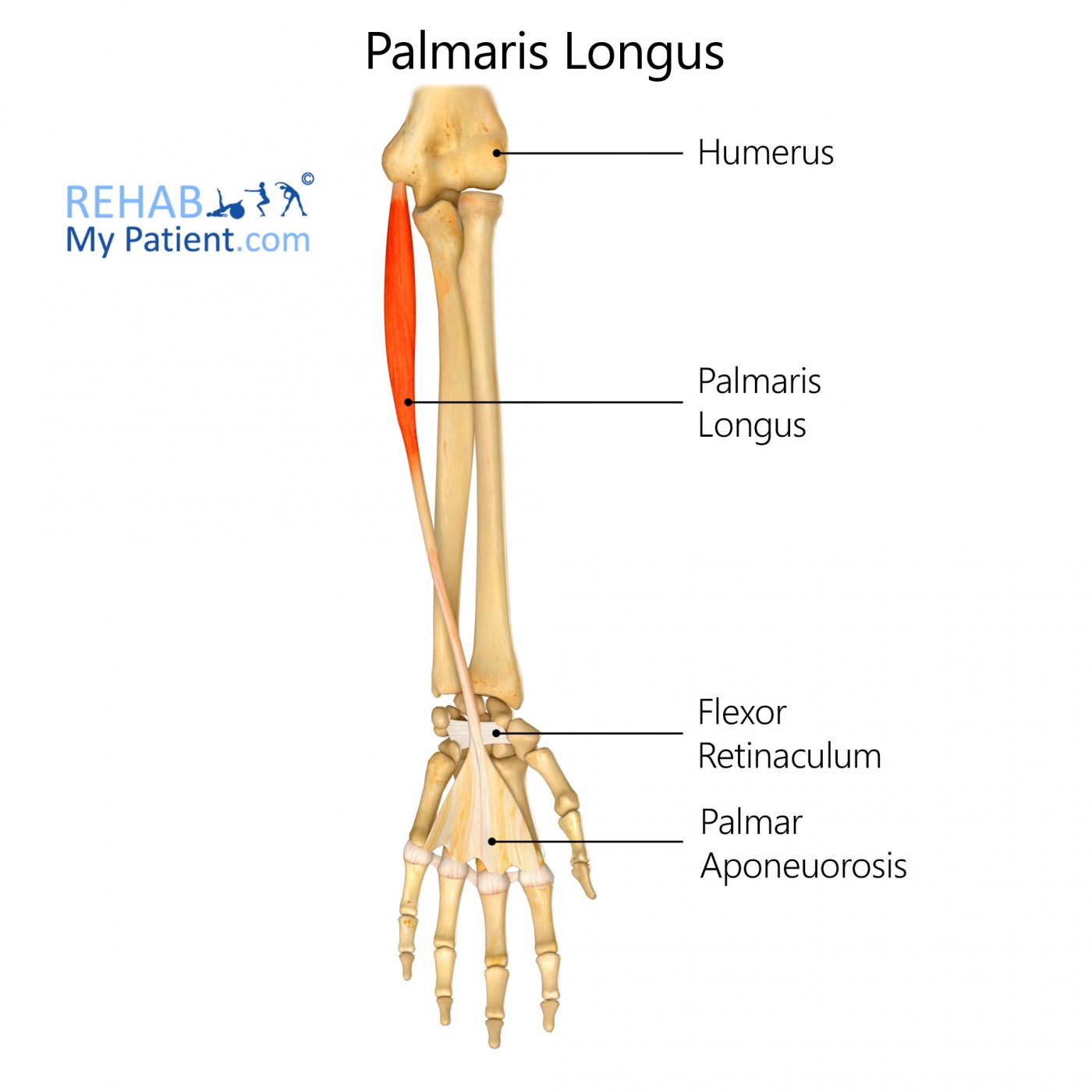
General information
The palmaris longus is a small tendon between the flexor carpi radialis and the flexor carpi ulnaris.
Literal meaning
Long muscle on the flat of the palm.
Interesting information
Unfortunately, not everyone is born with the palmaris longus - about 14 percent of the population is reported to have the absence of this muscle. Symptoms of an injury to this area include a prickling pain in the palm or base of the thumb, as well as the distal forearm. It may be difficult to grasp and use items, such as cups or tools. For strains of the palmaris longus, massage and stretching techniques are utilized. NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen, are taken to ease the pain and inflammation of the injured palmaris longus.
Plastic surgery, primarily reconstructive hand surgery relies of tendon grafts for which the palmaris longus satisfies the desired prerequisites of length, diameter, and availability. Using the palmaris longus will not result in any differentiation of functionality or aesthetics.
Origin
Medial epicondyle of the humerus through the common flexor tendon.
Insertion
Flexor retinaculum and palmar aponeurosis.
Function
Anchors the skin and fascia of the hand to keep it from sliding toward the phalanges.
Aids the flexion of the wrist.
Nerve supply
C7 and C8 median nerve.
Blood supply
Ulnar collateral arteries.
Relevant research
A study was conducted to examine the differentiation between populations who were found to have an absence of the palmaris longus. Although, the study did reveal some variation, there was not enough for statistical significance. The study was completed with 300 Caucasians, splitting evenly for gender. There does seem to be some variance according to ethnicity, however, that was beyond the scope of this study. Thompson, NW, Mockford, BJ, and Cran GW, May 2001, “Absence of the palmaris longus muscle: a population study”. The Ulster Medical Journal, V 70, N 1, p 22-24
It has long been suspected that ethnicity plays a key role in the absence or presence of the palmaris longus. This study examined if the Yoruba population of Nigeria has an increase in the number of people presenting the palmaris longus. They tested 600 participants, all from the Yoruba population. It was found that only 6.7% of the Yoruba population are missing the palmaris longus. The study concluded that ethnicity was a determining factor in the number of people presenting with the palmaris longus, with much higher numbers – up to 24% - of North American Caucasians missing the palmaris longus – than people of African and Asian origin.
Mbaka, O and Ejiwunmi, Adedayo B., May 2009, “Prevalence of palmaris longus absence – a study in the Yoruba population”. Ulster Medical Society V. 78(2)
Palmaris longus exercises
Wrist curls
While kneeling, lean over a bench while holding a lighter-weighted barbell or a low weight dumbbell in each hand. Hold the weight with palms facing up to the ceiling. Place the back of your forearms on the bench while your hands dangle over the far edge. Begin by keeping your wrists straight in line with the rest of your forearms. Slowly bend your wrists back as far as you can comfortably allow it. Then, slowly bring the weight back up and past the starting point, giving it a little contraction. Continue doing ten repetitions for three sets.
Sign Up
Sign up for your free trial now!
Get started with Rehab My Patient today and revolutionize your exercise prescription process for effective rehabilitation.
Start Your 14-Day Free Trial